Comprehensive Guide to Security Camera DVRs: Ensuring Safety with Advanced Technology
Security Camera Digital Video Recorders (DVRs) are fundamental components of modern security systems, offering robust solutions for monitoring and recording activities in various settings, from residential properties to extensive commercial spaces. The evolution of DVR technology has transformed how security is managed, making surveillance both more efficient and accessible. This article delves into the critical aspects of DVRs, providing insights to help you select and utilize these systems effectively.
Understanding Security Camera DVRs
What is a Security Camera DVR?
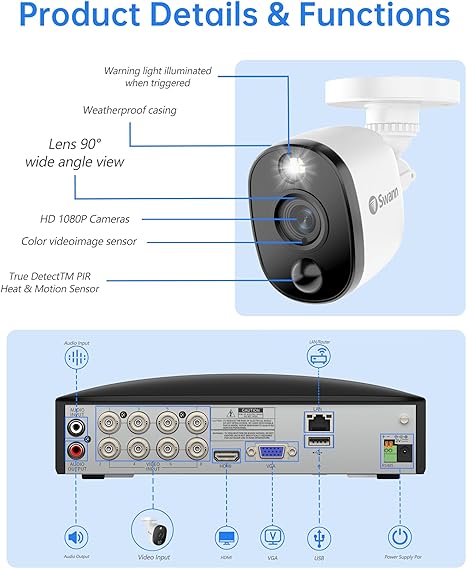
A Security Camera DVR (Digital Video Recorder) is a specialized system designed for the storage and management of video footage captured by analog security cameras. Unlike NVRs (Network Video Recorders) that require a network to receive video data directly from networked cameras, DVRs process video data at the recorder itself after receiving it through coaxial cables from the cameras. This technology makes DVRs an ideal choice for integrating into existing analog setups without the need for extensive re-wiring or network configurations.

Detailed Features of DVR Systems
Video Quality and Resolution
DVRs are capable of handling a wide range of video resolutions. Modern DVRs are typically compatible with HD video formats, including 720p, 1080p, and even 4K UHD, providing flexibility depending on the required level of detail and clarity for surveillance. The choice of resolution will directly impact the storage size and the clarity of the video, which is crucial for identifying faces or activities within the camera’s field of view.
Storage Capacity and Management
One of the critical features of DVR systems is their storage capacity, which can often be a determining factor in their deployment. Modern DVRs use hard disk drives (HDDs) to store large amounts of video data, and many units support additional slots for extra HDDs to expand the storage capacity. Advanced video compression technologies such as H.264 or H.265 help maximize storage efficiency by reducing the file size of the video without significant loss of quality. Efficient storage management also includes features like scheduled recording, motion-triggered recording, and overwrite functions, which help manage the disk space effectively by prioritizing new data over old.
Network Connectivity and Remote Access
While DVR systems are primarily designed for local storage and access, they also offer network connectivity options for enhanced flexibility. Users can configure their DVRs to connect to a network, enabling remote access via web browsers, dedicated applications on smartphones, and tablets, or even through third-party software. This feature is particularly useful for monitoring real-time video feeds from anywhere or retrieving stored video remotely, which can be critical in security operations or after a security event.

Types of DVR Systems Explained
Standalone DVRs
Standalone DVRs are all-in-one systems that are widely used due to their ease of installation and use. These systems include built-in software and sometimes hardware components necessary for video recording and monitoring in a single, compact device. They are typically plug-and-play, making them suitable for smaller setups or users who require a straightforward, reliable security solution.
PC-based DVRs
PC-based DVRs use a standard PC equipped with specialized software and a dedicated video capture card to process and store video data. This type of DVR allows for greater customization and scalability, suiting more extensive or specialized security needs. The performance of a PC-based DVR can vary significantly based on the specifications of the computer used, such as processor speed, RAM, and video capture hardware.
Hybrid DVRs
Hybrid DVRs represent a versatile recording solution, supporting both analog cameras and newer IP cameras. This capability makes hybrid DVRs an excellent option for users looking to upgrade their security systems incrementally. Hybrid systems allow for the integration of advanced IP technology without discarding existing analog infrastructure, providing a cost-effective pathway to modernize security systems.

Advanced Applications
In addition to basic recording and storage, many DVR systems offer advanced features like video analytics, which can include motion detection, tamper alerts, and other intelligent monitoring capabilities. These features enhance the DVR’s utility by automating security tasks and increasing the system’s overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Choosing the Right DVR for Your Needs
Factors to Consider When Selecting a DVR
Selecting the right DVR involves considering several factors:
- Storage Needs: Evaluate the amount of footage you need to store, which impacts the required storage capacity.
- Video Quality: Consider the importance of image clarity in your security objectives. Higher resolutions offer better clarity but may require more storage.
- Compatibility: Ensure the DVR system is compatible with your existing security equipment, particularly your cameras and monitoring setup.
Installation Tips for DVR Systems
Installing a DVR system can be straightforward if planned correctly:
- Positioning: Place the DVR in a secure, well-ventilated area to prevent overheating and potential tampering.
- Connecting Cameras: Connect analog cameras to the DVR using coaxial cables. Ensure connections are secure and protected from environmental factors.
- Power Setup: Implement a reliable power source, possibly with a backup system, to ensure continuous operation.
- Configuration: Configure settings such as recording schedules, motion detection areas, and alert notifications according to your security needs.
Benefits of Using DVR in Security Systems
Enhanced Security and Surveillance
DVR systems enable continuous recording and real-time monitoring, crucial for both crime prevention and evidence gathering. The ability to monitor live feeds and receive instant alerts to unusual activities provides a significant advantage in managing security threats.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
DVRs offer a cost-effective solution for extensive and scalable security setups. The initial investment might be significant, but the long-term benefits of robust security and minimal maintenance can outweigh the initial costs, especially when considering the potential loss prevention from theft or vandalism.

Integrating DVR with Modern Security Technologies
As security technology evolves, integrating Digital Video Recorders (DVRs) with modern advancements has become crucial in enhancing the effectiveness and convenience of security systems. This section explores how DVRs interface with newer technologies like smart home systems, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, providing users with a more cohesive and powerful security solution.
Smart Home Integration
Connectivity with IoT Devices
Modern DVR systems are increasingly designed to integrate seamlessly with the Internet of Things (IoT). This integration allows DVRs to connect with various smart devices in a home or business, such as door sensors, smart locks, and lighting systems. For instance, a DVR can be set up to start recording when a smart door sensor detects an opening, enhancing security through responsive, event-triggered actions.
Control via Smart Home Platforms
Integration with platforms like Google Home, Amazon Alexa, and Apple HomeKit enables users to manage their security systems via voice commands or through a unified smart home app. This convenience allows users to view live security footage, play back recorded videos, and arm or disarm their systems without needing to interact directly with the DVR hardware.
Advances in AI and DVR Systems
Facial Recognition and Object Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) significantly boosts the capabilities of DVR systems by enabling sophisticated features like facial recognition and object detection. DVRs equipped with AI can analyze video feeds in real time to identify known individuals or unauthorized access, sending instant alerts to the user. This technology not only enhances security but also adds a layer of automation that can help in managing access to secure areas.
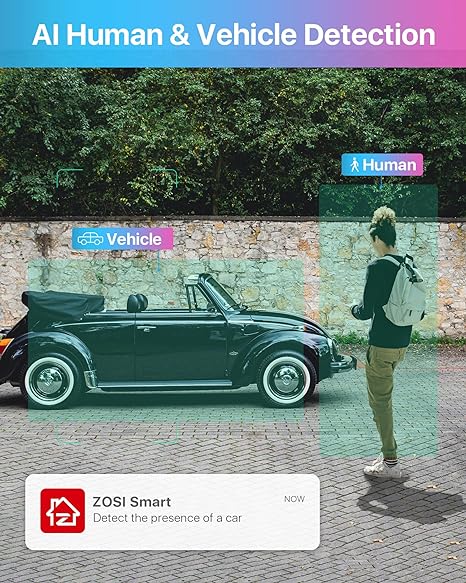
Behavior Analysis
AI can also be employed to analyze patterns of behavior over time, enabling the DVR to detect anomalies that may indicate suspicious activity. For example, if a person is detected loitering in a restricted area at an unusual hour, the system can automatically flag this as a potential security threat and alert security personnel.
Integration with Cloud Technology
Cloud Storage Solutions
While DVRs traditionally store video locally, the integration with cloud technology offers an additional layer of data backup and accessibility. Users can opt for hybrid storage solutions where video is stored both on local drives and in the cloud. This not only safeguards against data loss due to hardware failure but also facilitates remote access to video footage from any location, enhancing the flexibility of surveillance operations.
Enhanced Accessibility and Data Analysis
Cloud-enabled DVRs can utilize cloud computing for more than just storage; they can also leverage cloud processing power to perform more complex video analytics that would be too resource-intensive for local hardware. This capability allows for advanced data analysis, such as crowd counting or heat mapping, which can be invaluable for businesses looking to optimize space usage and improve customer service.

Cybersecurity Considerations
As DVR systems become more connected and integrated with internet-based technologies, cybersecurity becomes an increasingly critical concern. Ensuring that DVRs are equipped with the latest security measures, such as firewalls, encrypted communications, and regular software updates, is essential to protect against hacking and unauthorized access.
Future Outlook
The future of DVR integration with modern technologies holds promising advancements. Innovations in AI could lead to more predictive security measures, where systems not only react to known threats but can anticipate potential security breaches before they occur. Additionally, as smart home technology advances, DVRs could become even more integrated, managing a broader range of devices and responding more intelligently to environmental changes.
Integrating DVRs with modern security technologies not only enhances the capabilities of traditional surveillance systems but also provides users with a more dynamic, responsive, and manageable security solution. This progressive integration ensures that security systems remain effective in the face of evolving technological landscapes and emerging security challenges.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your DVR System
Regular Maintenance Tips
Maintaining and troubleshooting your Digital Video Recorder (DVR) system are essential aspects of ensuring that it operates efficiently and continues to provide reliable security surveillance. Proper maintenance can prevent common issues, while effective troubleshooting can quickly resolve problems that may arise, minimizing downtime and potential security risks. This section provides detailed insights into how to maintain and troubleshoot a DVR system effectively.
Periodic Checks
Regular inspections of your DVR system can help catch potential issues early before they develop into more serious problems. It’s advisable to perform a monthly check of all system components, including cameras, cables, power supplies, and the DVR unit itself. Look for signs of wear and tear, loose connections, or damage that could affect performance.
Clean and Dust-Free Environment
Keep the DVR unit in a clean, dust-free environment to prevent overheating and ensure optimal functioning. Dust accumulation can clog vents and fans, leading to increased heat and potentially causing hardware failure. Regularly cleaning the DVR’s exterior with a soft, dry cloth and ensuring that ventilation areas are unobstructed can significantly prolong the unit’s lifespan.
Software and Firmware Updates
Manufacturers often release updates to the software and firmware of DVR systems to fix bugs, patch security vulnerabilities, and add new features. Keeping your DVR updated with the latest software version is crucial for maintaining security and functionality. Schedule regular updates as part of routine maintenance, and check the manufacturer’s website or support channels for information on the latest releases.
Backup Important Data
Regularly back up important video data to an external hard drive, cloud storage, or another secure location. This practice protects your data in case of hardware failure, accidental deletion, or data corruption. Set up an automatic backup schedule if your DVR supports it, or perform manual backups periodically, depending on the importance and volume of the data.

Troubleshooting Common DVR Issues
If your DVR system suddenly stops working, check the power supply first. Ensure the power cords are securely plugged in and that there are no tripped breakers or blown fuses. Power surges can also cause the system to malfunction; consider using surge protectors to safeguard your equipment.
Video loss or degradation in video quality can be due to several factors:
- Camera Connections: Check all connections between the cameras and the DVR to ensure they are secure and undamaged. Loose or corroded connectors can interrupt the video signal.
- Camera Settings: Incorrect configuration settings on the cameras or DVR can affect video quality. Ensure settings like resolution, frame rate, and compression are appropriately configured for your specific needs.
- Cable Quality: Use high-quality cables that are suitable for video transmission over long distances without degradation.
System Crashes or Freezing
If the DVR system crashes or freezes, a hard reboot might resolve the issue. However, if this occurs frequently, it could indicate deeper problems like overheating, insufficient power supply, or hardware failure. Check if the DVR unit is hot to the touch, ensure it is well-ventilated, and consider having a professional inspect the unit if the problem persists.
Firmware Issues
Corrupted firmware can cause various operational issues, including system instability and functionality loss. If you suspect firmware issues, try resetting the DVR to its factory settings, which can often resolve software-related problems. If this doesn’t help, you may need to re-install the firmware, following the manufacturer’s guidelines closely.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many common issues with DVR systems can be resolved through basic troubleshooting, more complex problems or consistent failures should be addressed by a professional technician. If you experience recurring issues or if troubleshooting steps do not resolve the problems, it’s advisable to contact the manufacturer’s support or a professional security system service provider.
By adhering to these maintenance and troubleshooting guidelines, you can ensure that your DVR system remains reliable and functional, safeguarding your property and assets effectively. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the life of your security system but also enhances its performance, providing peace of mind in knowing that your surveillance system is always operational when you need it most.
Legal Considerations and Privacy
It’s essential to be aware of local laws regarding surveillance and privacy. Ensuring that your use of a DVR system complies with these laws can prevent legal complications, which might include restrictions on audio recording and the placement of cameras in public or shared spaces.
Future Trends in DVR Technology
The future of DVR technology is closely tied to advancements in storage solutions, data compression methods, and AI capabilities. Emerging trends suggest even greater integration with cloud technologies and more sophisticated analytical capabilities, which could further transform security surveillance.
Conclusion
Investing in a quality DVR system enhances security, provides peace of mind, and adapts to evolving technology and needs. With the right setup, maintenance, and understanding of legal considerations, a DVR can serve as a cornerstone of a robust security system.




